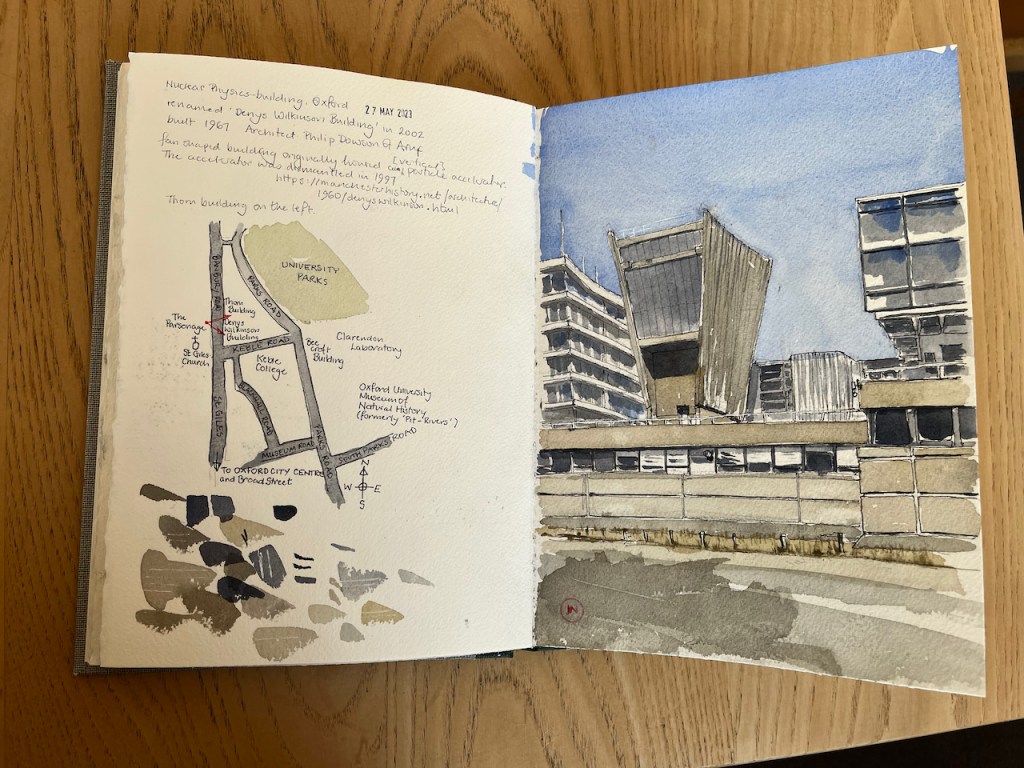
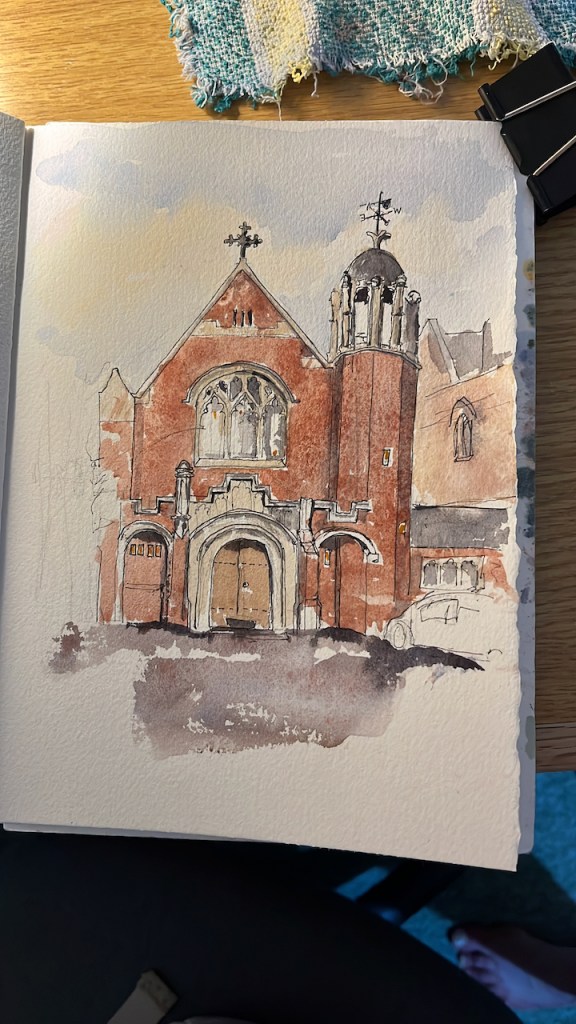
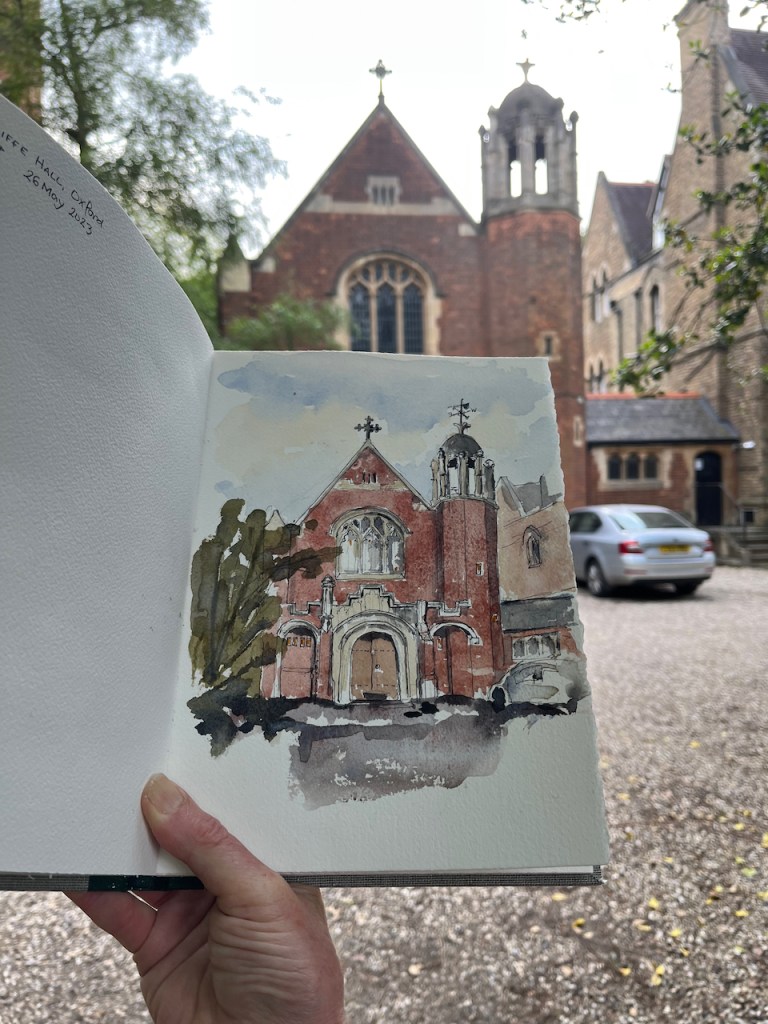
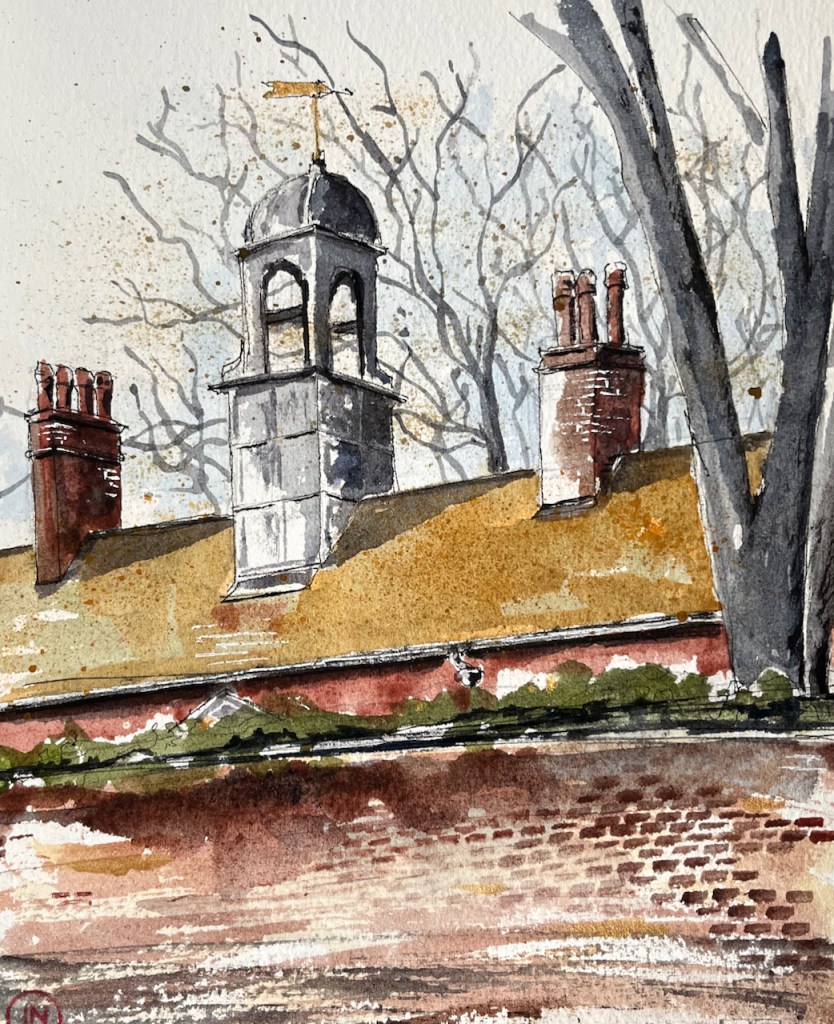
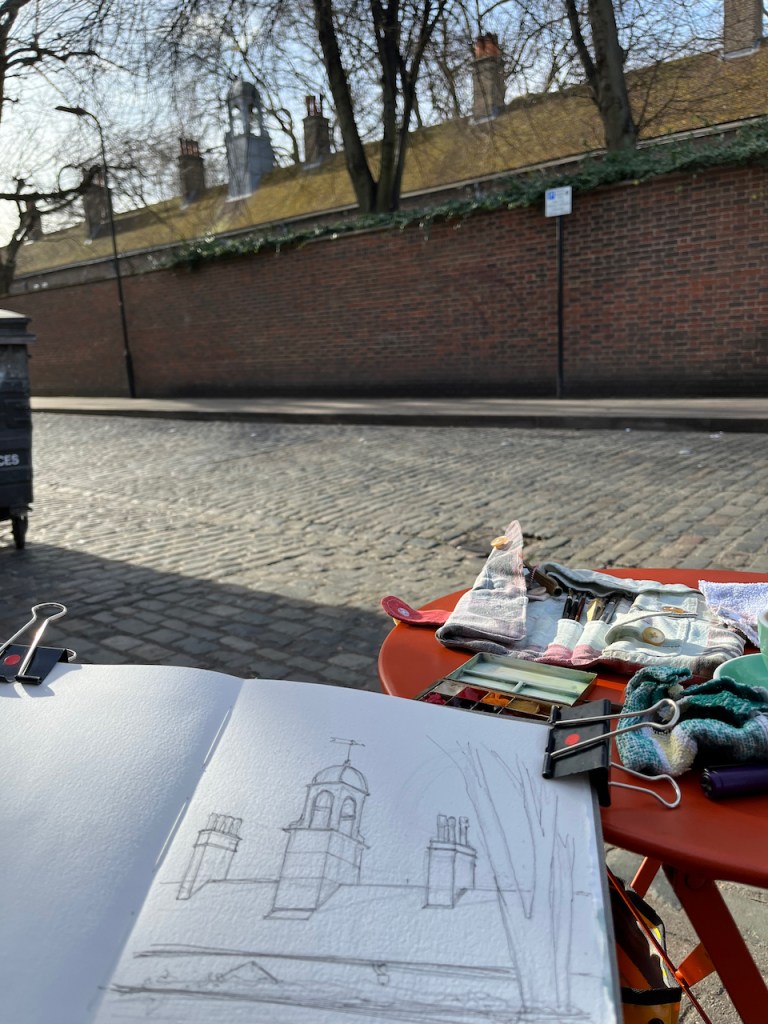
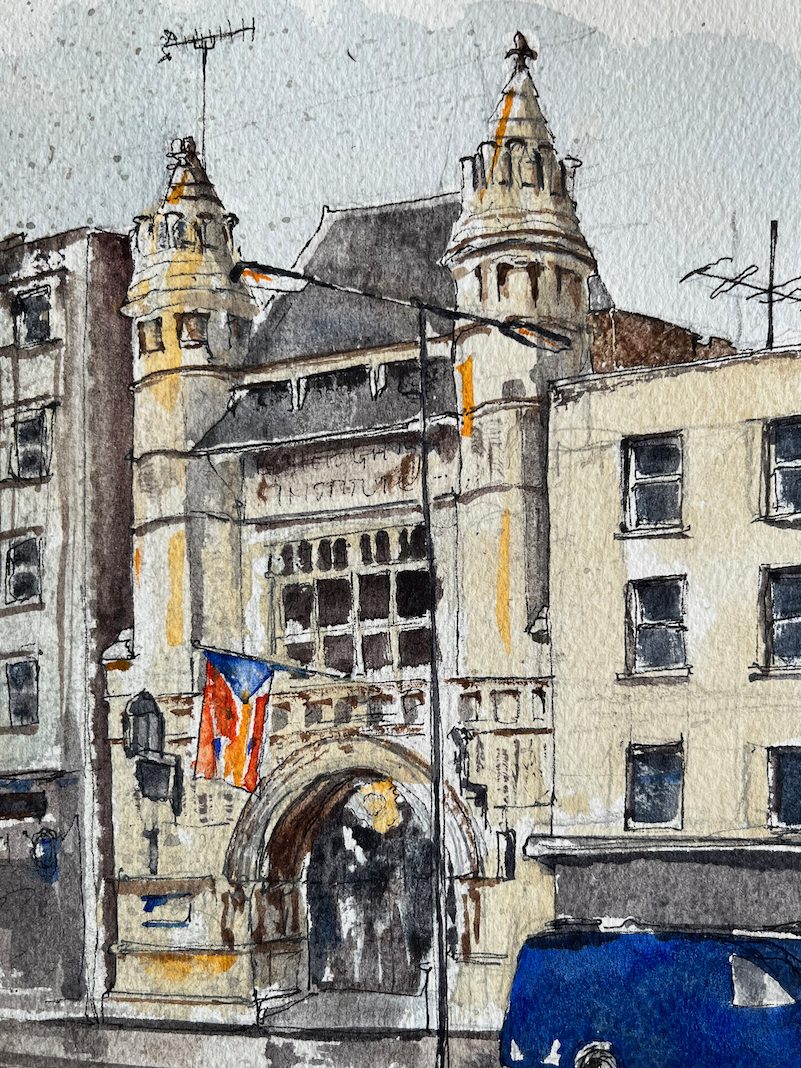
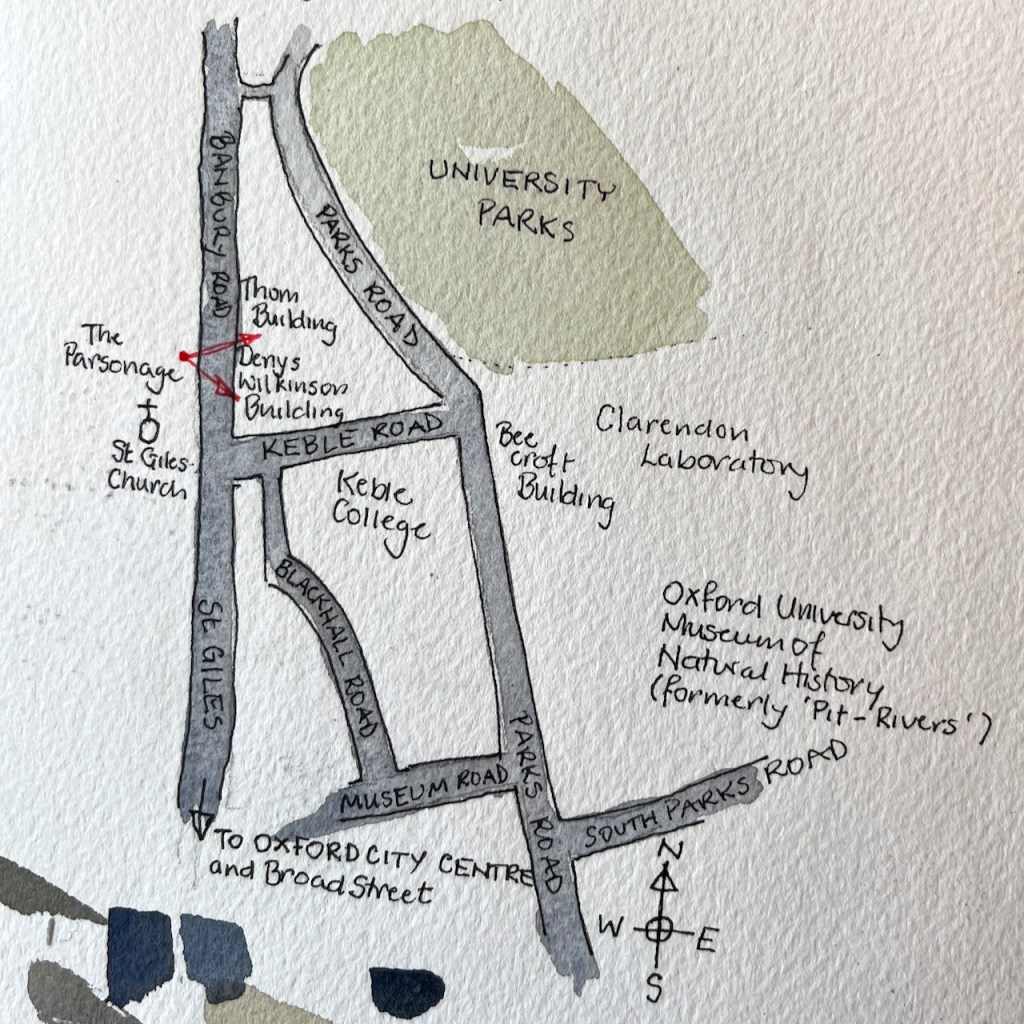
Here is the University of Oxford Nuclear Physics building, seen from the Banbury Road.
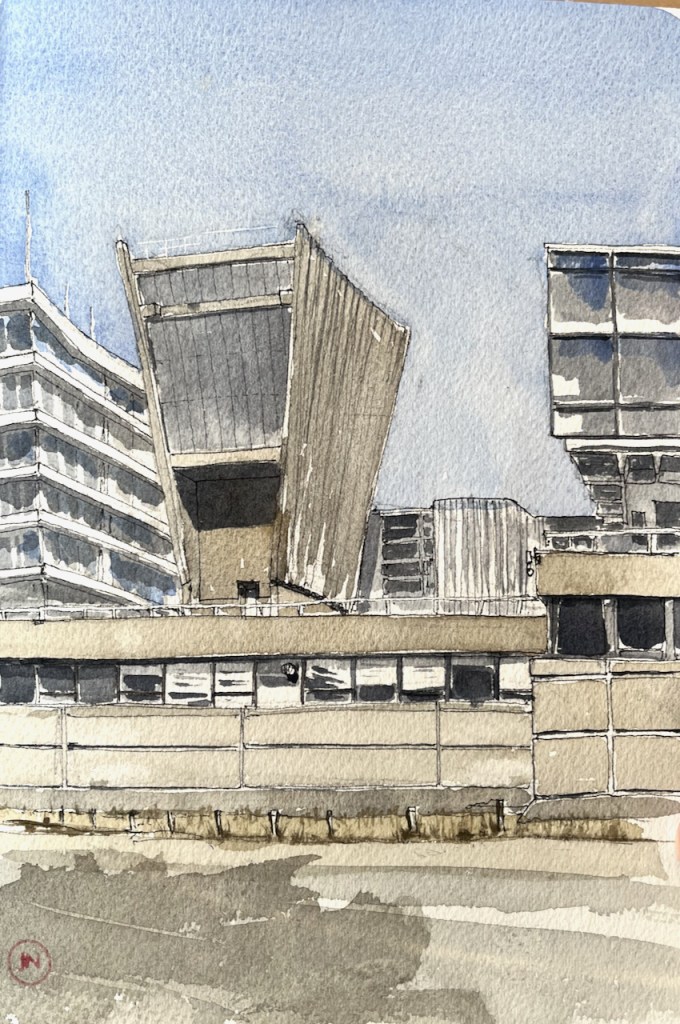

The building was renamed the “Denys Wilkinson Building” in 2002. It was built in 1967 to the designs of architect Philip Dowson of Arup. The fan-shaped structure originally housed a Van der Graff particle accelerator, now dismantled. [https://manchesterhistory.net/architecture/1960/denyswilkinson.html]
Professor Wilkinson (1922-2016) was the Head of the Nuclear Physics Department from 1962-1976.
The building on the left is the “Thom Building” which houses the Engineering Department. This building had a marvellous “paternoster” lift in the 1970s. (Note 1). This is a lift with single compartments, which operates in a continuous loop, like rosary beads, hence the name. You simply stepped into one of the slowly moving compartments and were carried up or down.
Here is work in progress on the drawing:


The fan-shaped structure is a rare example of brutalism in Oxford. St Catherine’s College is another example.
Ought we to treat the Denys Wilkinson building and St. Catherine’s College as a celebrated chapter in Oxford’s aesthetic history, or as evidence of a period better forgotten?
Caitriona Dowden -writing in the Cherwell, 26th October 2020 [https://cherwell.org/2020/10/26/oxfords-eyesores-brutalisms-place-among-the-dreaming-spires/]
A celebrated chapter in Oxford’s aesthetic history, I think. here are some details of the design, for brutalism enthusiasts like me:
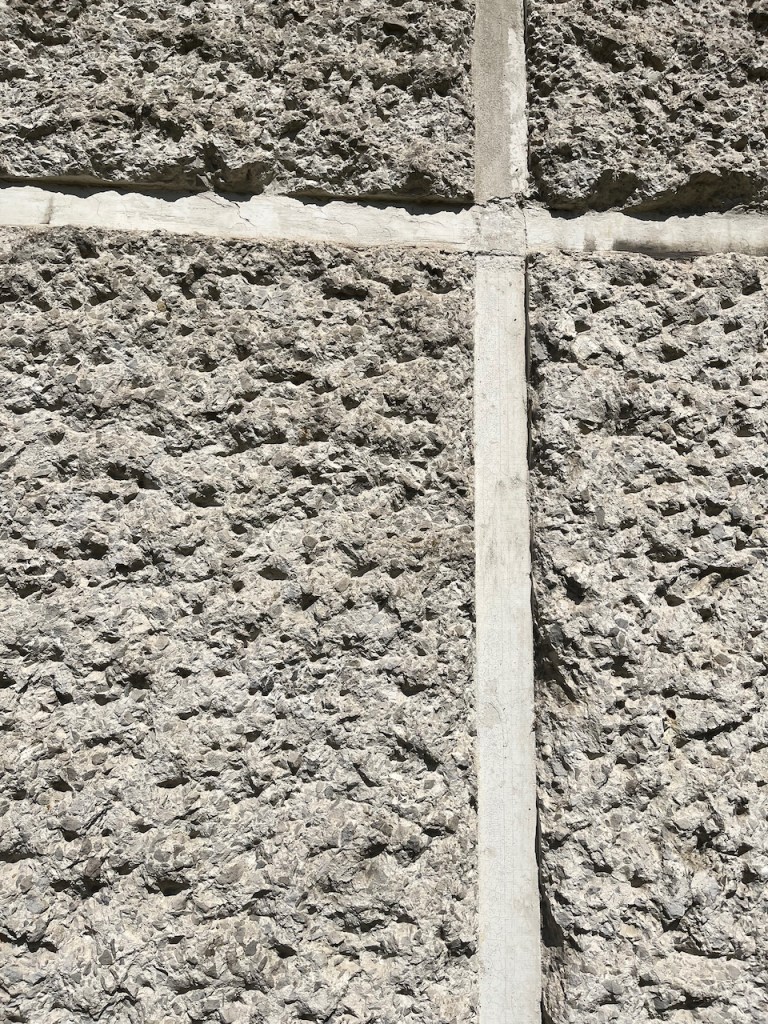
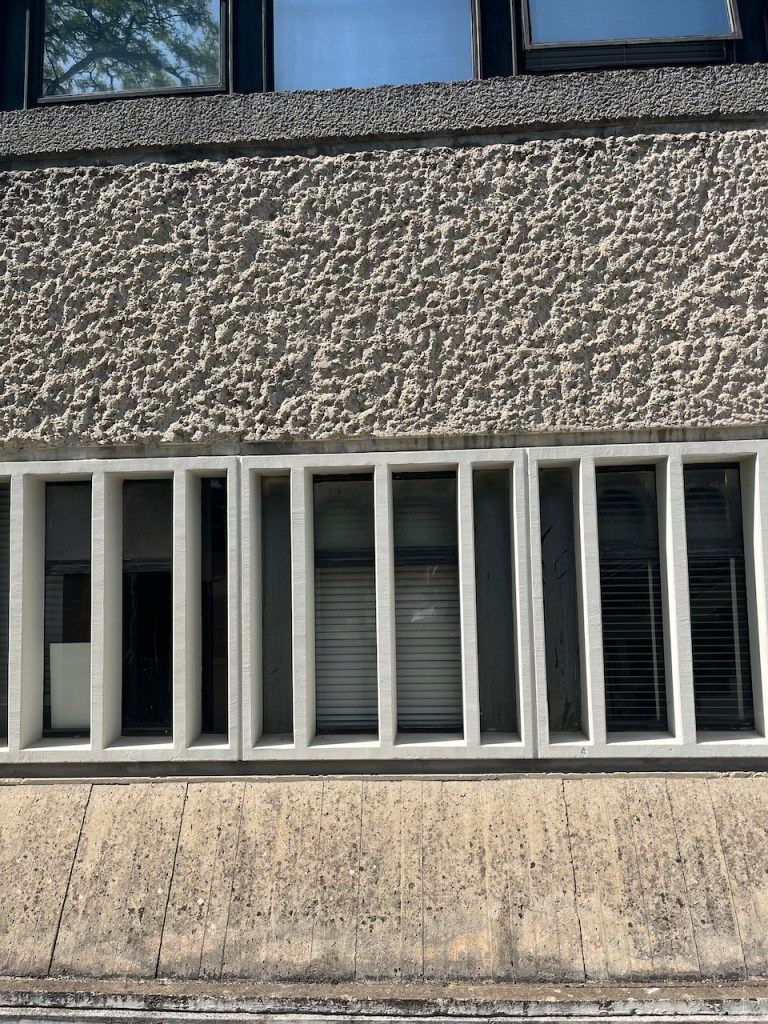



Note 1: Alan Knight writing of his memories of the department confirms my recollection: https://www.soue.org.uk/souenews/issue2/jottings.html. The paternoster was replaced by two ordinary lifts in the 1980s.